


These studies draw the attention to the lack of concurrence between the clinical and pathological pictures, which therefore is deemed as a major impediment for the diagnosis accuracy, with a significant impact in endodontic practice. The mainstream publications report rather few studies focused on the relationship between the pathological and clinical status in dental pulp diseases. Hence, inflammatory pulp diseases are a major challenge for the endodontic specialists, requiring both practical experience and theoretical knowledge. Nevertheless, an immediate therapeutic intervention is essential for the maintenance of pulp vitality. Therefore, its direct inspection and palpation as well as the pathological assessment become difficult tasks. The loose pulp tissue is protected by enamel and dentin, structures with a high degree of mineralization. Acute or chronic inflammatory reactions of the pulp, occurring as a result of exposure of the pulpodentinal tissue, are caused by various invasion modalities involving or not the dentinal tubules. Dental pulpitides represent a separate class of endodontic pathology initiated, in most cases, by a progressive dynamic process of dental caries. The clinical diagnosis relies on the correlation of information regarding the inflammatory state of dental pulp described by the patient through clinical symptoms, mainly pain, which together with other paraclinical data (dental radiographies) provide the basis for a therapeutic decision. Pulp pathology is the generic term used in the description of pulp diseases as a morphofunctional ensemble. On the basis of the predominant pathological aspects, namely, acute and chronic pulpitis, we consider that the classification schemes can be simplified by adequately reducing the number of clinical entities. We also obtained significant differences between acute pulpitides and inflammatory infiltrate and calcifications and between chronic pulpitides and inflammatory infiltrate, collagen deposition, and calcifications. No significant differences were established between the score values for inflammatory infiltrate intensity, collagen depositions, calcifications and necrosis, and acute, respectively chronic pulpitides. The results of the statistical analysis revealed the correlations between clinically and pathologically diagnosed acute/chronic pulpitides. The clinical and morphological correspondence was noted for 35 cases (68.62%), whereas inconsistency was recorded for 16 cases (31.38%). The morphological features were semiquantitatively assessed by specific score values.
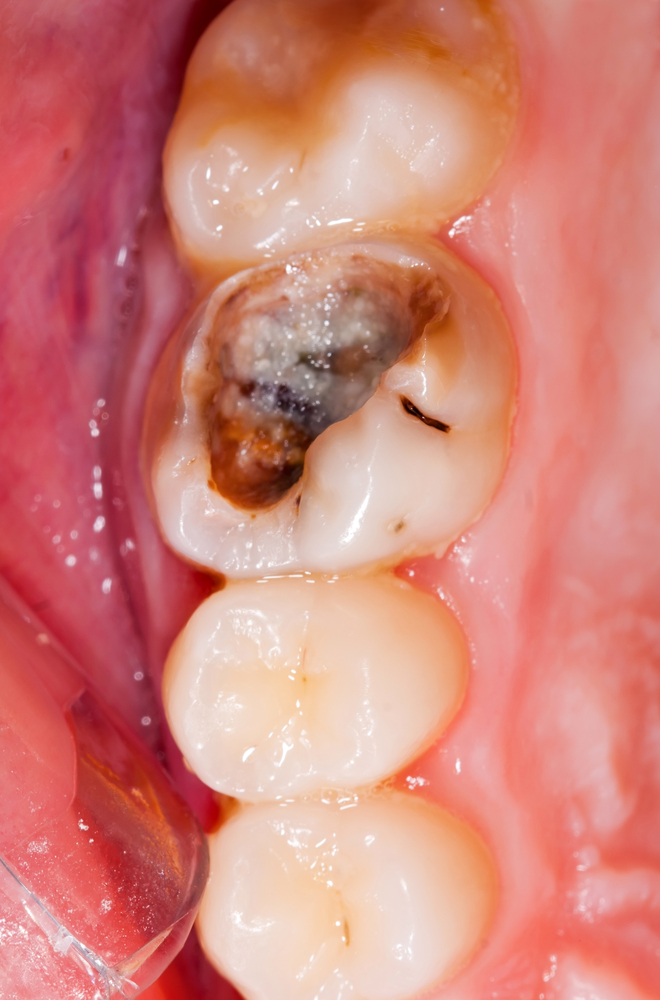
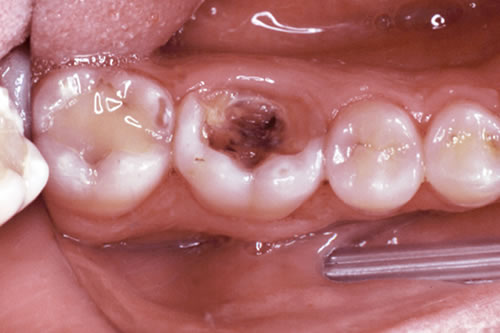
Pulpectomies were performed for 54 patients with acute and chronic irreversible pulpitides and for 5 patients (control group) with orthodontic extractions. Within this anatomical context, our study aimed to evaluate the correlation between dental pulp lesions and clinical diagnosis. Consequently, the direct examination as well as pathological evaluation of dental pulp is difficult. Dental pulp represents a specialized connective tissue enclosed by dentin and enamel, the most highly mineralized tissues of the body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
